Engineering is truly a noble profession, without it life would not exist
as we know it. These 10 engineers are remarkable in the sense that they
did not have any blueprints or guides to go by, but they set out to
accomplish what had never been done before. All they had was their
genius and passion for bettering humanity with their creations. Without
them, we probably would not have had the many things we now take for
granted.

He is regarded by some as the father of computer science. He is also credited with breaking the German Enigma code during WWII, which made victory possible. In the years following the war he made numerous contributions in software creation. Time magazine named him as one of the most important people of the 20th century.
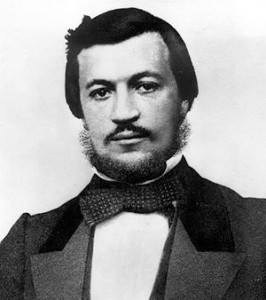
Despite having developed the engine, it was Otto’s peers such as Gottlieb Daimler and Karl Benz who made practical applications of the technology, forever changing how people move all over the world.

Tesla moved to America in 1884 to work with Thomas Edison, another remarkable engineer. Within weeks of working for Edison, he indicated that he could improve the efficiency of the company’s generators by 25%. Edison promised Tesla a $50,000 bonus if he achieved this feat. Within weeks Tesla delivered on his promise – and Edison reneged on his, telling young Tesla, “You don’t understand our American humor.”
According to some legends he was instrumental in defending his native Syracuse from Romans by his clever use of machines to keep enemies at siege. He also calculated an approximation for pi and developed many mathematical insights without which modern engineering would be impossible.
The watt unit of power is named after James Watt. He is credited for measuring the power of his steam engine: his test with a strong horse resulted in his determination that a “horsepower” was 550 foot-pounds per second. Subsequent calculation by Watt resulted in one horsepower equaling 746 watts.
 This
man could have started the Industrial Revolution in 50 AD with the
invention of the Aeolipile, a form of steam or jet engine where jets of
steam spin a ball. However, he failed to realize what the device could
do, and thought of it as nothing but a toy. Some have speculated that
the abundance of slave labor negated any need for a labor-saving device,
so no one applied his device in the manner of the Industrial
Revolution. Hero also wrote many works on subjects ranging from
pneumatics to mathematics to physics.
This
man could have started the Industrial Revolution in 50 AD with the
invention of the Aeolipile, a form of steam or jet engine where jets of
steam spin a ball. However, he failed to realize what the device could
do, and thought of it as nothing but a toy. Some have speculated that
the abundance of slave labor negated any need for a labor-saving device,
so no one applied his device in the manner of the Industrial
Revolution. Hero also wrote many works on subjects ranging from
pneumatics to mathematics to physics.
 Before
Wilbur and Orville discovered what would later become the safest mode
of transport, they were bicycle mechanics with a passion for
kite-flying. The crucial insights from both fields would later propel
them to victory in the race to the sky.
Before
Wilbur and Orville discovered what would later become the safest mode
of transport, they were bicycle mechanics with a passion for
kite-flying. The crucial insights from both fields would later propel
them to victory in the race to the sky.
Most prototypes of the time could not stay in the air long enough after taking off. The Wright brothers however understood that stability was crucial in overcoming this challenge. After several experiments using kites and gliders, they created a pulley system that altered the shape of the wing in mid-flight, increasing and decreasing the speeds. The Wright brothers were also the first to look at propeller design and aerodynamics, profoundly changing the world.
 Henry
Ford realized that he would a more efficient way to mass produce cars
in order to lower the price. He looked at other industries and found
four principles that would further their goal: interchangeable parts,
continuous flow, division of labor, and reducing wasted effort. Ford put
these principles into play gradually over five years, fine-tuning and
testing as he went along. In 1913, they came together in the first
moving assembly line ever used for large-scale manufacturing. Ford
produced cars at a record-breaking rate forever changing the automobile
industry.
Henry
Ford realized that he would a more efficient way to mass produce cars
in order to lower the price. He looked at other industries and found
four principles that would further their goal: interchangeable parts,
continuous flow, division of labor, and reducing wasted effort. Ford put
these principles into play gradually over five years, fine-tuning and
testing as he went along. In 1913, they came together in the first
moving assembly line ever used for large-scale manufacturing. Ford
produced cars at a record-breaking rate forever changing the automobile
industry.
 Edison
is the most prolific inventor in history, holding a record 1,097
patents. He developed the phonograph, incandescent light bulb, stock
ticker, motion picture camera and projector, and hundreds more. He also
created the first electrical plant and distribution infrastructure.
Without these inventions, modern life is almost inconceivable.
Edison
is the most prolific inventor in history, holding a record 1,097
patents. He developed the phonograph, incandescent light bulb, stock
ticker, motion picture camera and projector, and hundreds more. He also
created the first electrical plant and distribution infrastructure.
Without these inventions, modern life is almost inconceivable.
 Perhaps
the biggest visionary of all time, Leonardo foresaw everything from the
helicopter to the tank to the submarine. Modern engineers have proven
that many of his designs, including bridges, hang-gliders,
transmissions, parachutes, and more would have worked had they been
built. There have been few individuals in the history of engineering who
have designed so many revolutionary devices that actually worked. For
having this remarkable vision and intelligence, Leonardo qualifies as
the most remarkable engineer of all time.
Perhaps
the biggest visionary of all time, Leonardo foresaw everything from the
helicopter to the tank to the submarine. Modern engineers have proven
that many of his designs, including bridges, hang-gliders,
transmissions, parachutes, and more would have worked had they been
built. There have been few individuals in the history of engineering who
have designed so many revolutionary devices that actually worked. For
having this remarkable vision and intelligence, Leonardo qualifies as
the most remarkable engineer of all time.
10. Alan Turing

Alan Turing
Every time you use a computer, it is in part because Alan Turing made significant contributions to make computing possible. Alan Turing developed the binary architecture now used in all computers, as well as much of the theory behind computers.
He is regarded by some as the father of computer science. He is also credited with breaking the German Enigma code during WWII, which made victory possible. In the years following the war he made numerous contributions in software creation. Time magazine named him as one of the most important people of the 20th century.
9. Nicolaus Otto
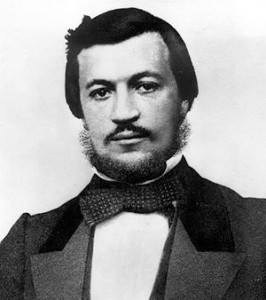
Nicolaus Otto
Nicolaus Otto was a German inventor credited with developing the four-stroke or Otto-cycle engine which sparked the development of the motor care. His Otto-cycle engine worked in four steps; drawing in fuel and air, compressing the mixture, igniting it and expelling the exhaust. This Otto-cycle is still used in the internal combustion engines that run all of our cars today.
Despite having developed the engine, it was Otto’s peers such as Gottlieb Daimler and Karl Benz who made practical applications of the technology, forever changing how people move all over the world.
8. Nikola Tesla

Nikola Tesla
Every electrical engineer should have a picture of Nikola tattooed somewhere on their bodies. Maybe not a tattoo but at least have a picture of him hanging in their office. Tesla’s inventions make him arguably the greatest electrical engineer of all time. His inventions include fluorescent lighting, the Tesla coil, the induction motor, and 3-phase electricity. He developed the AC-current generation system comprised of a motor and a transformer.
Tesla moved to America in 1884 to work with Thomas Edison, another remarkable engineer. Within weeks of working for Edison, he indicated that he could improve the efficiency of the company’s generators by 25%. Edison promised Tesla a $50,000 bonus if he achieved this feat. Within weeks Tesla delivered on his promise – and Edison reneged on his, telling young Tesla, “You don’t understand our American humor.”
7. Archimedes
It was Archimedes who came up with the simple yet clever idea of determining an object’s volume by measuring the amount of water displaced by the object. Other inventions credited to him include the catapult, levers and pulleys, and the Archimedean Screw, a device used to raise water for irrigation or mining.According to some legends he was instrumental in defending his native Syracuse from Romans by his clever use of machines to keep enemies at siege. He also calculated an approximation for pi and developed many mathematical insights without which modern engineering would be impossible.
6. James Watt
James Watt was an enthusiastic inventor whose improvement of the steam engine sparked the Industrial Revolution. During the 1760s he devoted most of his time to improving the efficiency of steam engines. The result was a machine that become very popular that Watt is sometimes mischaracterized as the inventor of the steam engine. Watt’s many mechanical advances earned him several patents, and his engines were used for coal mining, textile manufacturing, transportation and a host of other industrial uses.The watt unit of power is named after James Watt. He is credited for measuring the power of his steam engine: his test with a strong horse resulted in his determination that a “horsepower” was 550 foot-pounds per second. Subsequent calculation by Watt resulted in one horsepower equaling 746 watts.
5. Hero of Alexandria

Aeolipile
4. Wilbur and Orville Wright

Wilbur and Orville Wright
Most prototypes of the time could not stay in the air long enough after taking off. The Wright brothers however understood that stability was crucial in overcoming this challenge. After several experiments using kites and gliders, they created a pulley system that altered the shape of the wing in mid-flight, increasing and decreasing the speeds. The Wright brothers were also the first to look at propeller design and aerodynamics, profoundly changing the world.
3. Henry Ford

Henry Ford
2. Thomas Edison

Thomas Edison
1. Leonardo DA Vinci

Leonardo DA Vinci


No comments:
Post a Comment